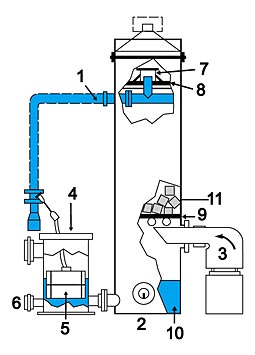
Decarbonization PlantsDecarbonation is the process of free carbon dioxide removal from water. A decarbonator is a device using which reduction of carbon dioxide concentration in water is achieved by blowing air at CO2 distribution between the liquid (water) and gaseous (air) phases. Tower decarbonators are the most widespread.Decarbonators are used in the first stage of iron removal from underground water passed through clarifying filters. It also can be applied as an intermediate stage for the removal of СО2 residue after a hydrogen cycle. Operating Principal of the Decarbonators
This diagram shows a decarbonators model without an additional water inlet. A water inlet is a storage tank which contains the water reserve; the decarbonator is installed upon it. The water inlet is necessary for the equipment’s continuous operation during commencement, any technical interruptions or periodic operations. The decarbonator’s operation is possible either with a water inlet or without one. If you order a decarbonator without a water inlet then we will install the decarbonator on an iron or reinforced concrete tank with an additional inner coating. Our specialists will help you select the necessary water inlet’s volume. Water is sprayed or distributed above the ordered or disordered nozzle made of plastic or any stainless material (it consists of rings, chords, etc.) in decarbonation plants. Air is supplied by the ventilator under the perforated plate that serves as a support for the nozzle. Air and water are circulated by countercurrent. Degassed water is stored in the reservoir that is located below the contact column. The residual C02 concentration in the liquid phase depends on the temperature, water flow rate, type and amount of nozzles and the air flow. It is possible to obtain residual C02 concentration which is very close to equilibrium concentration (3-5 mg/l) using properly designed systems. Decarbonators have such advantages, as:
To choose the decarbonator, please complete the questionnaire or contact us. |